Summary
- New EEPROM implementation
- Prusa Connect Local (WebUI)
- Stop print function fixed
- Remote print - OctoPrint
- Adjustment to Mesh Bed Levelling
- New color scheme for active button
- Improved movement near the axis end
- Revised file sorting
- Adjustments to e-steps
Detailed description
New EEPROM implementation
Due to historical reasons, the previous firmware releases were using two EEPROM implementations - one provided by stock Marlin, the other for Prusa-specific persistent data. However, this implementation was causing synchronization issues and it was decided to unify both EEPROMs into one. As a result, the support for Marlin's EEPROM is now disabled and upon the reboot, all the Marlin settings are always set to the default values.
Any specific adjustment of those values should be part of the G-code. The only variables from Marlin allowed to be stored in the EEPROM are the Live Adjust Z and PID calibration. The EEPROM further contains Ethernet settings, the filament type and the information, whether the Wizard was successfully finished.
Each variable is now saved independently, unlike in Marlin, where saving one variable resulted in an update to all other variables. The data integrity is now guaranteed by the CRC32. If an error during the check is detected, the EEPROM is set back to the factory defaults, thus the printer has to be calibrated again.
The old and new implementations of the EEPROM are compatible, but only in case of an upgrade. If the user decides for a downgrade from the 4.0.5 to an older firmware a factory reset is recommended.
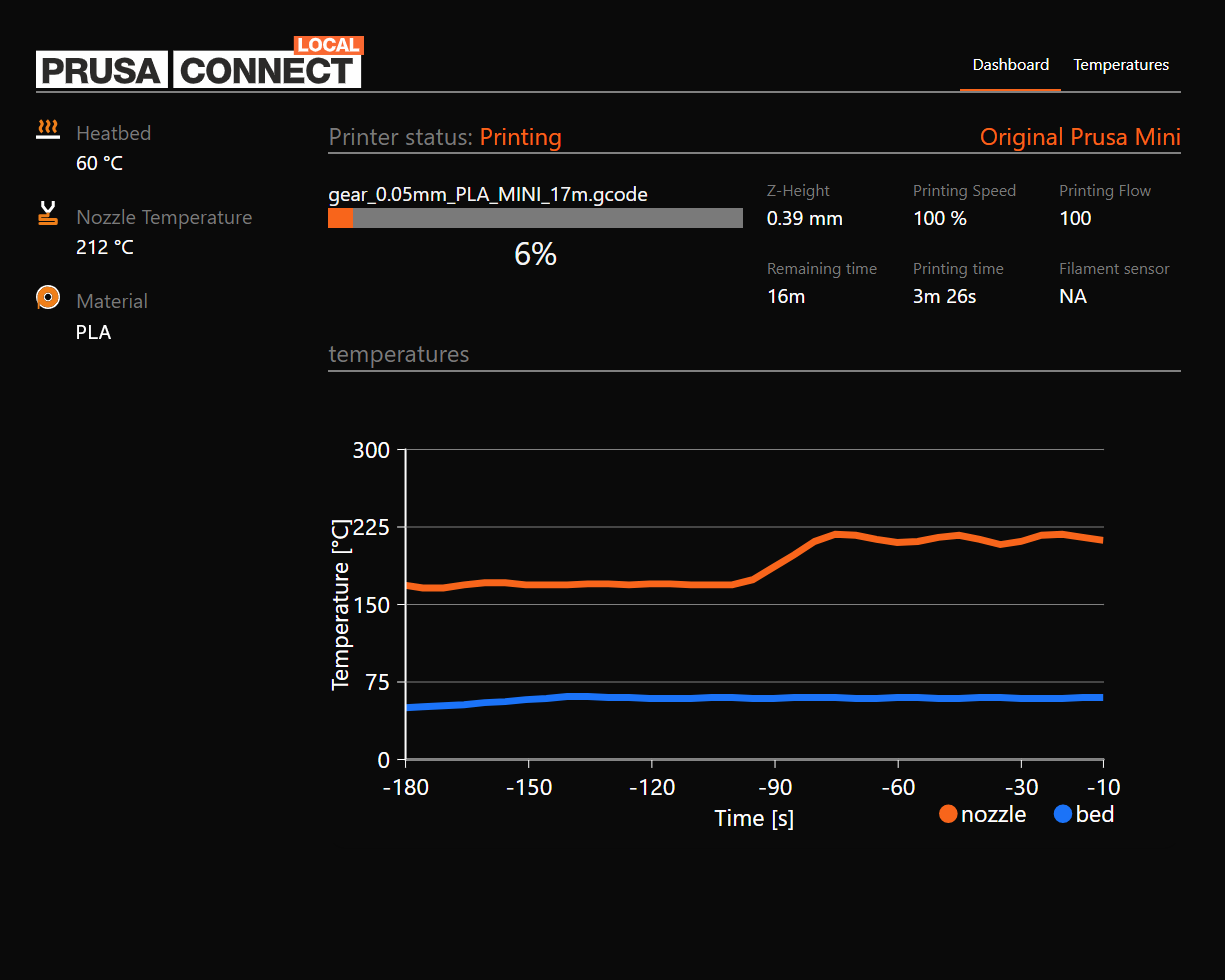
Prusa Connect Local (Web UI)
Starting with this release, there is a brand new web interface called Prusa Connect Local, designed to provide remote monitoring capabilities. The current version provides an overview of the following:
- Name of the printed G-code
- Temperature of the heatbed and nozzle
- Type of the loaded material
- Current print speed
- Current height of the Z-axis
- Printing / Remaining time
There are more features to come and the web interface will be further updated in the upcoming releases.
Stop print function fixed
The Stop print function was sometimes using incorrect coordinates while parking the print head or the heatbed, this resulted in multiple attempts to reach the end of the axis and chattering sound. This issue occurred mostly while printing large objects and the printer had to travel longer distances. This is now fixed.
Remote print - OctoPrint
When you start a remote print over the popular app OctoPrint, the printer becomes locked and a dialog is displayed on the screen. This is for safety reasons. To control the printer (e.g. temperature adjustment) during the remote print, please use the OctoPrint app or web interface. However, in a critical situation, the user is still able to reboot the printer using the hardware button situated under the screen.
Note: The "Live Adjust Z" adjustment during the print is now not available while using the OctoPrint. It will be addressed in the final release.
Adjustment to Mesh Bed Levelling
In some scenarios, we have observed improper readings during Mesh Bed Levelling (MBL). This can be caused for example by a slightly misaligned print steel sheet. To address this issue and possible errors in the future, the outer edges for the MBL were moved 5 mm towards the center of the heatbed. The printing area remains unchanged.
A new color scheme for active button
In order to improve the clarity of dialog windows, the color scheme of the actively selected buttons was changed to an orange background and black font. A typical example is the YES/NO dialog.
Improved movement near the axis end
In the case of the print head or the heatbed being too close to the edge of its axis, the printer sometimes incorrectly detected the current position and continued the movement with a higher power, forcing the motor to skip a step. The algorithm responsible for the detection of the end of the axis was improved to prevent these situations.
Revised file sorting
The file sorting algorithm was improved to handle the files on the USB drive based on the time of the last change. Since every operating system (Windows, macOS, Linux) handles this differently, the printer compares the following times (file creation time and file modification time) and selects the most recent one.
The new sorting algorithm also handles specific situations like:
- Extracting an old G-code from a ZIP archive
- Updating an existing G-code file directly on the USB drive
Adjustments to e-steps
Based on the internal testing it was discovered that there is a slight under-extrusion during the print. To compensate for this behavior, the e-steps value was adjusted by 2.5 %.